
The rectus femoris has an additional role in stabilizing the hip joint and aiding in the flexion of the thigh. This group of muscles has a common function.
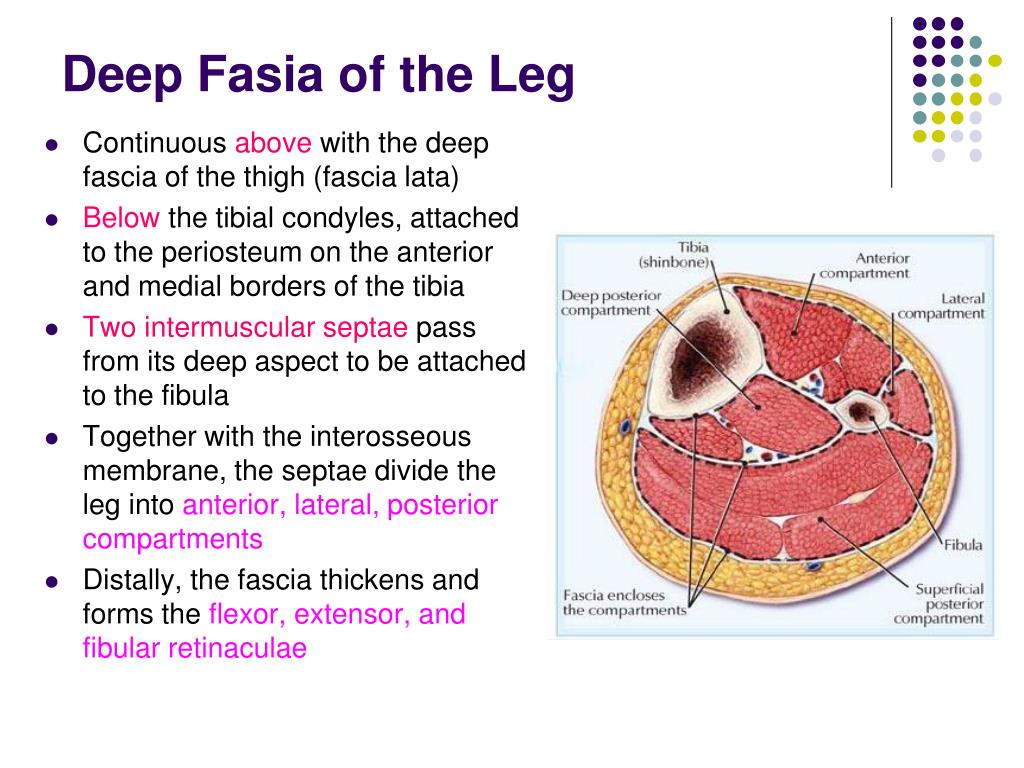
The quadriceps femoris is one of the strongest muscle groups in the body that covers the anterior aspect of the femur. The quadriceps include four large muscles, rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius. It originates from the anterior superior iliac spine and runs superficially to the quadriceps muscles, and inserts on the superomedial surface of the tibia via the pes anserinus. The sartorius is a long band-like muscle that runs lateral to medial, crossing the anterior aspect of the thigh. It also aids in the flexion of the knee joint and the medial rotation of the leg in this position. The sartorius flexes, abducts, and laterally rotates the thigh at the hip joint. It joins the psoas muscles traveling deep to the inguinal ligament and inserts on the tendon of the psoas major and the distal part of the lesser trochanter of the femur. The iliacus originates from the iliac crest, iliac fossa, ala of the sacrum, and anterior sacroiliac ligaments. The psoas minor found anterior to the psoas major originates from the T12 through L1 vertebrae and then inserts on the pectineal line. The psoas major then passes down through the pelvis and under the inguinal ligament to insert on the lesser trochanter of the femur. The psoas major originates from the transverse processes of the T12 to L5 vertebrae. These muscles work together to flex the hip joint as well as stabilize this joint during standing. The iliopsoas is made up of the psoas major and minor and the iliacus. Originating from the superior pubic ramus and inserting on the pectineal line of the femur. The pectineus is a small square muscle that is found in the superomedial area of the thigh. The pectineus adducts, flexes, and assists in medial rotation of the thigh. Inferior to the inguinal ligament, the saphenous opening allows for the passage of the great saphenous vein. The aponeurosis of the tensor fasciae latae and gluteus maximus muscles also contribute to the IT tract. The iliotibial (IT) tract is a thickened portion of the fascia that is found on the lateral aspect of the thigh. The fascia lata is the deep fascia surrounding the thigh, and this fascia layer acts to limit the outward expansion of the thigh muscles. The posterior intermuscular septum separates the medial and posterior compartments. The medial intermuscular septum separates the anterior and medial compartments. The lateral intermuscular septum separates the anterior and posterior compartments. The intermuscular septae are extensions of the fascia lata and attach to the linea aspera of the femur. įascial compartments separate the muscles of the thigh to create the compartments outlined above. The medial or adductor compartment is composed of the adductors of the thigh. The posterior or flexor compartment is the prime extensors of the hip and flexors of the knee. The anterior or extensor compartment is responsible for flexion of the hip and extension of the knee. The three compartments of the femoral region each have a distinct function. These muscles arise from the ischial tuberosity and the femur and insert on the medial tibia and lateral fibula.

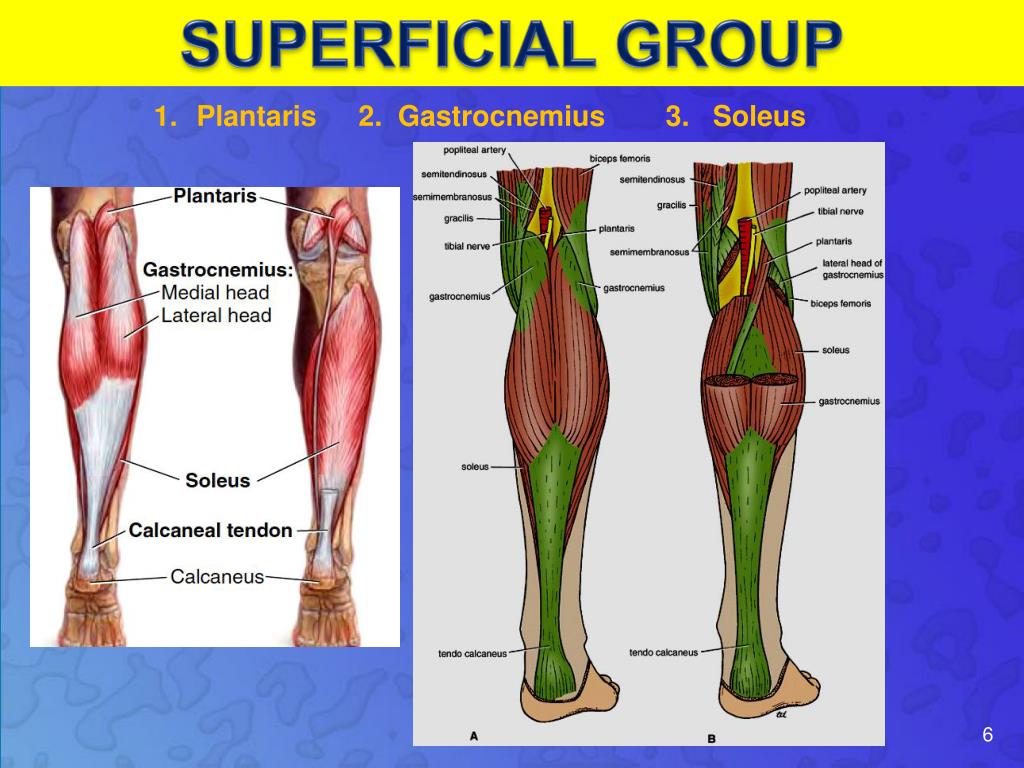
The posterior compartment is made up of a group of muscles called the hamstrings, including semitendinosus, semimembranosus, and biceps femoris. These muscles originate near the anteroinferior external surface of the bony pelvis and insert at the linea aspera. The medial compartment is made up of the adductor magnus, adductor longus, adductor brevis, gracilis, and obturator externus. These muscles arise from the hip, spine, and proximal femur. The anterior compartment includes pectineus, iliopsoas, psoas minor, iliacus, sartorius, and quadriceps muscles.
Each compartment is separated from the others by an intermuscular septum that runs from the fascia lata to the linea aspera of the femur. The muscles of the femoral region of the lower limb are divided into three compartments the anterior or extensor, medial or adductor, and posterior or flexor compartments.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
